How to use Backup for Workgroups to backup multiple Windows ServersBackup for Workgroups makes it easy to backup the Windows Servers on your network. It takes just 4 steps.
That's it - with just 4 steps you can begin backing up the Windows Servers on your network with Backup for Workgroups. Backup for Workgroups supports Windows Server 2019 / 2016 / 2012 / 2008 / 2003 both 32 bit and 64 bit and the Small Business versions of Windows Server. It includes an open a file add-on that allows the backup process to backup all open files on the Windows Server including locked files such as Exchange Database files, SQL Server Database files, and Domain Controller's Active Directory. Let's go through the 4-step process in more detail below. Follow along on your computers. Step 1 - Select the computer to act as the Backup ServerBackup for Workgroups is a client / server application. You need to select one of your computers to be the Backup Server. This computer can be a Windows Server or a Workstation, as long as it is running Windows 2000 or higher you can use it as your Backup Server. The Backup Server needs access to enough disk based storage such as internal drives, external USB / eSATA drives or access to NAS or network shared storage. When possible, try to install the Backup Server software on a computer with a relatively fast processor to keep your backups running as fast as possible. Backup for Workgroups will take advantage of multi-core CPUs so we recommend dual or quad core processors. Backup for Workgroups does not use a lot of memory so 2 to 4 GB of RAM is normally just fine. The key thing to keep in mind when selecting your Backup Server computer is its access to storage. If you want the fastest running backups and restores possible, then you need to use the fastest storage - internal SATA drives. We strongly recommend using internal SATA drives as the backup storage media. You can use NAS or network storage, but these units tend to have finicky rights settings that can take a little trial and error to setup until you get Windows and the Linux OS on the NAS unit to play nicely with each other. The computer you choose to run the Backup Server software can be a computer that you wish to include in the backup process or not. It is common to select one of the computers that you are planning to backup to operate as both the Backup Server and a Backup Client. Be aware that when the other computers are performing their backups the Backup Server computer will be under load. This may not be an issue since most backups run during the night. Let's assume you have an Exchange Server, a SQL Server, a File Server and a Domain Controller. You may choose to use the domain controller as the Backup Server since it is most likely lightly used at night. Step 2 - Select Storage DriveBefore downloading and installing Backup for Workgroups on the computer you selected as the Backup Server, you will need to have your backup storage media in place. You can use an internal hard drive, an external drive such as USB or eSATA, or a NAS or network share. You can also span your storage across dissimilar drives if the amount of storage space you need is larger than one hard drive's capacity. Backup for Workgroups supports just about any storage so long as Windows sees the storage device as a drive. Here are the most commonly used backup storage types. Find the type that matches what you plan to use and click on that line item below.
Using Internal Hard Drives to hold your backup dataUsing internal hard drives to hold your backup data is the optimal backup storage configuration. This type of backup configuration provides the most reliable solution because the backup storage drive(s) is/are always available and accessible. Unlike USB drives and NAS units that can be powered down separately from your Backup Server, internal drives are always available concurrently with your running Backup Server. Another benefit of using this backup configuration is that it makes it easy to comply with off-site storage requirements by using an external USB drive as a mirror drive. When you use internal storage drive(s) for the primary storage location, the internal drive(s) is/are continuously available and you can use a transient external drive as a mirror. In our example below, we have purchased a new, bare drive, sometimes called an OEM drive. This is just a simple SATA drive with a large capacity. We opened up the computer that we have selected to be the Backup Server and inserted the additional hard drive as marked by the red arrow below.
Now we can put the computer case back together and power up the Backup Server. Since this drive is an empty drive it will need to formatted. To format a new, blank, internal hard drive:1. At the Backup Server's Desktop - right click on "Computer" and choose "Manage." 2. At the Server Management screen expand the Storage section and select Disk Management. Windows will pop-up a wizard, to walk you through the process of formatting the new drive and assigning it a drive letter. If this wizard does not pop up, right click on the drive and choose Format.
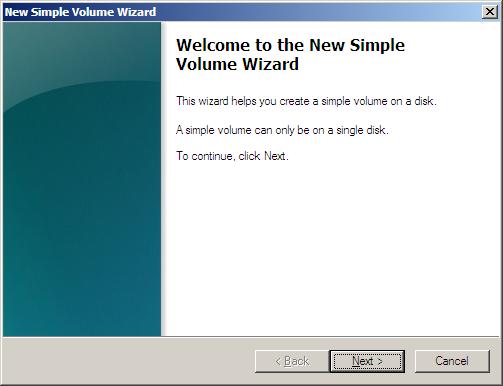
Press Next to navigate from the Welcome screen to the New Simple Volume Wizard as seen below.
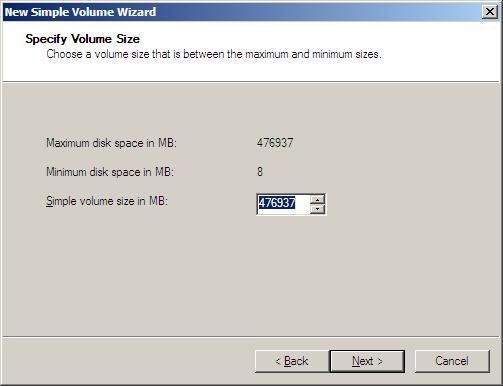
Enter the amount of the drive to setup for this volume. Normally you would use the default to use the entire drive space. Press Next to continue.
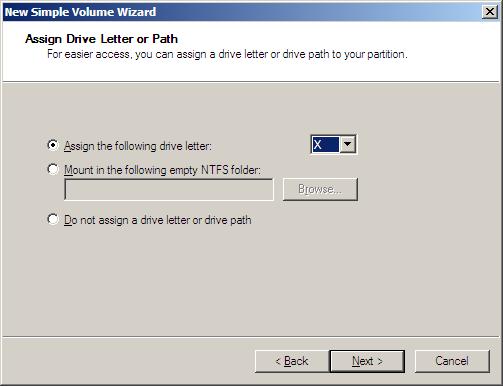
You can now specify a drive letter for the new drive. We suggest a drive high in the alphabet for several reasons. The first reason is when there is a gap in the drive letter sequence it works like a comment to yourself that this drive is for a specific reason - namely to be used for backup data not routine file storage. The second reason for setting a high drive letter is to avoid conflicts with other drives or USB devices that may not be attached at this time. Press Next.
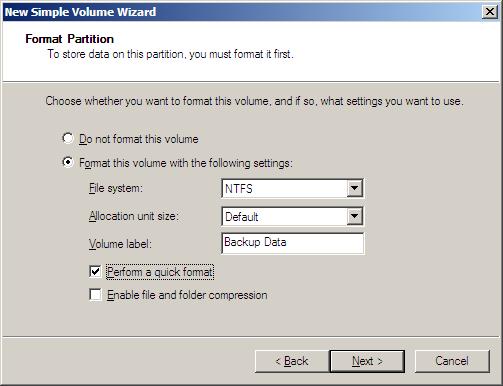
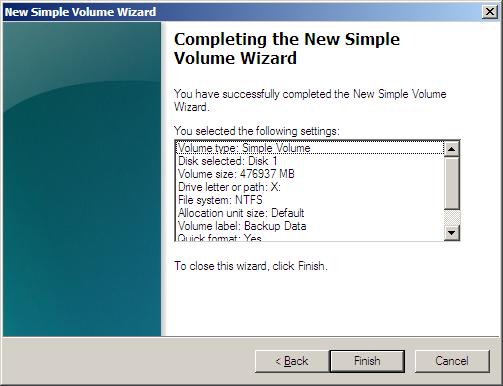
Choose to format the drive as NTFS. You can enter a Volume Label that is a comment to yourself. We recommend using a volume label such as "Backup Data". Since most drives today are high capacity drives, you may want to perform a quick format. A regular format can take over an hour on a drive over 1 TB. Press Next.
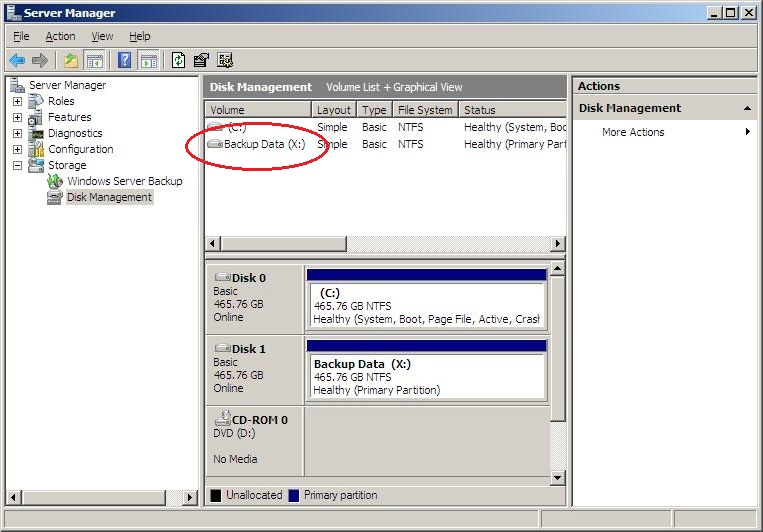
Review the summary information that is presented. If you wish to make any changes you can press Back to go through the process again. Otherwise, Windows is now ready to format the new drive. Press Finish to begin formatting the drive. When Windows has finished formatting the new drive, you will return to the Server Manager screen, which was still open before we used the Wizard to format the drive.
Now you can see that the new drive appears in the list above and it is ready to use. You are finished with setting up your internal storage drive and are ready to proceed to Step 3 in the Backup for Workgroups installation process. Click here to Jump to Step 3 to download and setup Backup for Workgroups. Using External Hard Drives to hold your backup dataMany people do not want to open up their computer to install an internal drive, which makes using external drives a convenient alternative. There are many vendors that offer inexpensive external USB or eSATA drives that you can purchase and attach to the Backup Server. When you choose to backup to an external drive, you will need to format the drive as NTFS and assign it a drive letter. We recommend using a drive letter that is high in the alphabet, letters that are closer to Z than A. Windows assigns drive letters to devices as they are attached to your computer. When you select a drive letter for your primary storage drive to be a letter that is high in the alphabet, it will not conflict with other USB devices such as flash drives, which Windows assigns to the next available letter that is low (or close to C) in the alphabet. Example: Here is a generic Windows Server that we plan to use as the Backup Server. We have attached an external USB drive as seen in the picture below:
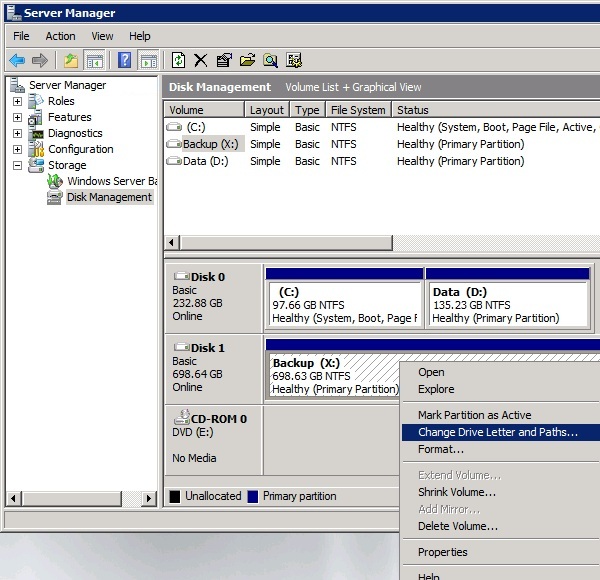
Now that you have your hardware in place, you are ready to format the external USB drive and assign it a drive letter that is high in the alphabet. In our example, we will use the letter X. To format your external USB storage drive and assign it a drive letter1. At the Window's Desktop - right click on "Computer" and choose "Manage." 2. At the "Server Management" screen expand the Storage section and select 'Disk Management." 3. Make sure the drive is formatted as NTFS. In the screen shot below we can see the drive is formatted as NTFS. If this is reported as FAT32, then Right click on the drive and choose Format. Then proceed to format the drive as NTFS. Note you can perform a quick format to save time.
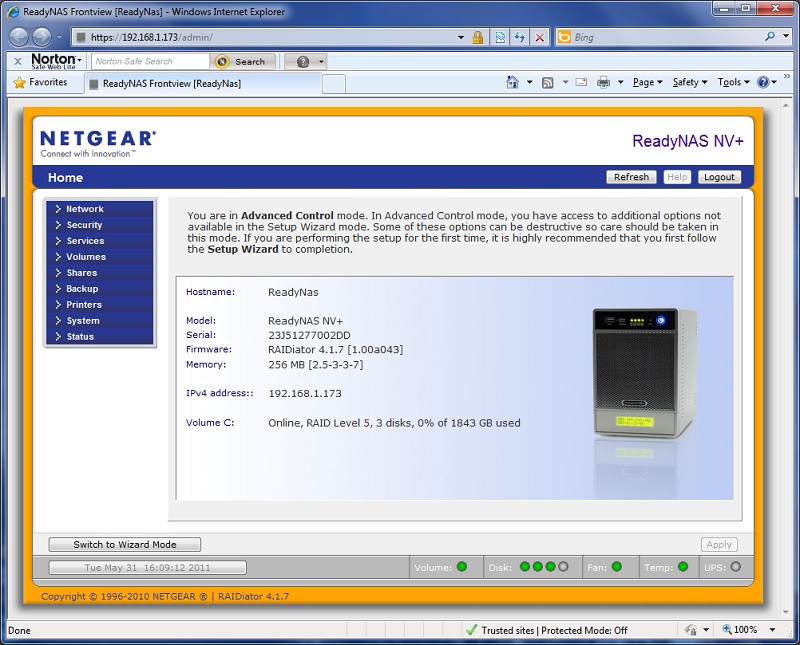
4. Assign the drive letter. In the center section of the screen right click on the USB drive and choose "Change Drive Letter and Paths." 5. Select the drive letter X: (or any letter that is high in the alphabet) and save your changes. The USB drive is now ready to be used to store the backup data. Click here to Jump to Step 3 to download and setup Backup for Workgroups. Using Network Shares and NAS units to hold your backup dataIf you have an existing NAS unit or a network share to another computer with the appropriate free storage space, you can use it to store your backup data. NAS units are handy because you can add storage to a network at will. If you have a computer that has a large amount of storage you can use a network share to that computer. Whether you are using a network share to another computer or a NAS unit, the setup is basically the same. In our example below we are using a NAS unit but if you have a network share to another computer just follow the same steps substituting the other computer in place of our example NAS unit. In our example below we have selected a Windows computer to be the Backup Server and we also have a NetGear ReadyNAS on the network with this computer.
The most common issues with NAS units is rights and permissions. When you are using a NAS unit to hold your backup data, the first thing you need to do is properly configure the rights and permissions to grant Backup for Workgroups access to the NAS unit. To Configure Rights and Permissions on your NAS device:1. Go to the computer you have selected to be the Backup Server. 2. You need to access the NAS unit's configuration panel. Most NAS units contain a web interface that is used to configure their settings. Open a web browser and enter the IP address of the NAS unit or its name. 3. Login into the NAS Unit.
4. Most NAS unit will create a default share. In the case of our example, the NetGear Ready NAS creates a share named Backup and gives everyone full access. If your NAS unit does not create network shares then follow these steps to add a network share to the NAS unit.
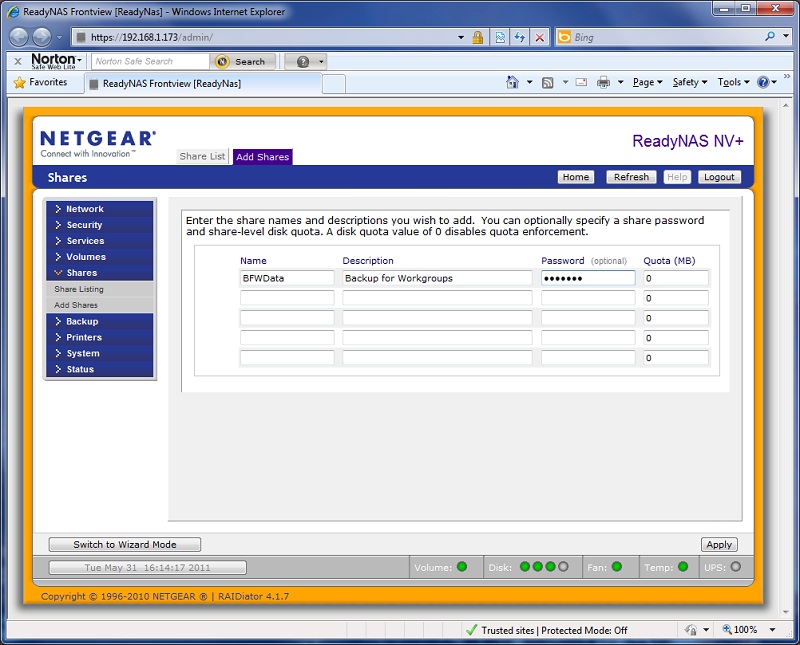
5. Go to the Add Shares option on your NAS device. In our example, we used the menu on the left to expand Shares and select Add Share. The ReadyNAS displays a grid. Enter the name of the share you want to create. If you do not provide a password, everyone will have open access to the backup data. Once you create your share press the Apply button to save your changes. 6. Go to the Share Listing option in the menu to verify the settings for this network share.
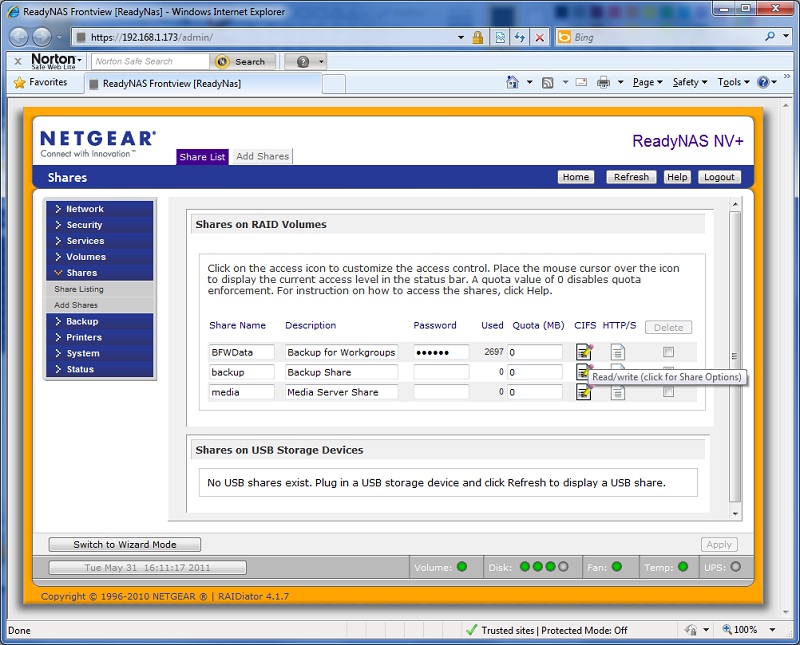
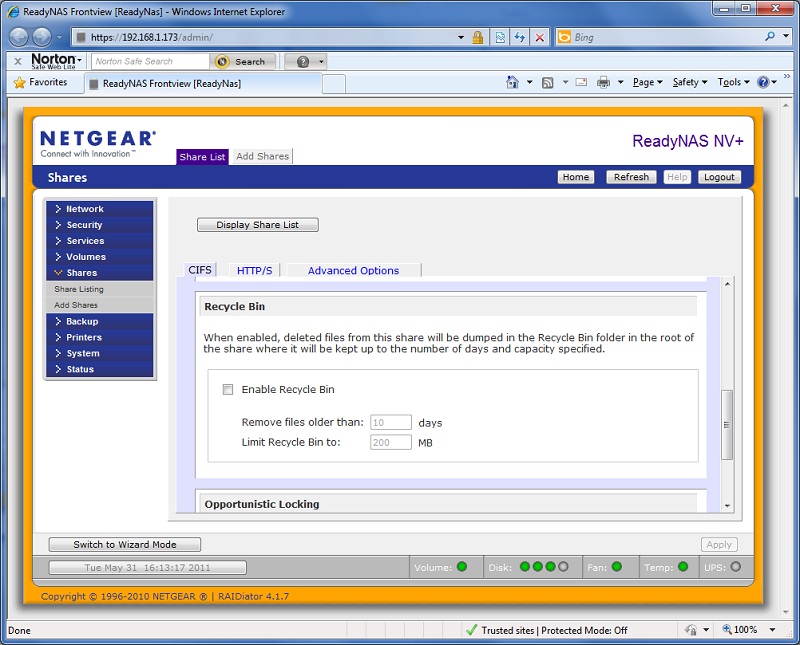
You want to verify that the network share has read/write access in order to grant full permissions to Backup for Workgroups. In this case, when we hover over the CIFS section, we can see a tool tip that shows Read / Write access. This is what Backup for Workgroups needs; it needs to be able to read/write files, create and delete files and have the ability to change the names of files. 7. Be sure to verify that the Recycle Bin is disabled for this network share. You DO NOT want to activate the recycle bin. When the recycle bin is active the NAS will keep copies of files that are deleted. This will quickly fill up the NAS unit and you will run out of disk space at the unit. To make sure the recycle bin is turned off, click on the icon under CIFS for the share we created. When you click on that icon, the following screen appears.
8. Now you can make sure the Recycle Bin is unchecked / unticked so that it is disabled. Some NAS units call the Recycle Bin the Trash Box. Again, if you do not disable the Recycle Bin on the NAS you will run out of disk space. 9. At this point, you should now have your NAS unit configured and ready to use. You can verify this by pressing the Start button at Windows and select Network. This will show your NAS in the list of Network devices. Double click on the NAS unit and you should see the list of shares- which should be the same as you had seen in the NAS configuration screen. Double click on the share we created and if you provided an account name and password, Windows will ask you for that account name and password to login to the network share. Enter the account name and password and log into the share. Step 3 - Download and Setup the Backup for Workgroups Backup ServerAt this point you should have selected the computer that you plan to use as the Backup for Workgroups Backup Server and you also have the backup storage unit in place, formatted and ready to use. You are now ready to download the Backup for Workgroups setup program. Go to the computer that you have selected as the Backup for Workgroups Backup Server. Click on the Download Now button below. Enter your contact information then return to this page to continue following the instructions. 1. Go to the Backup Server. 2. Run the bfwsetup program.
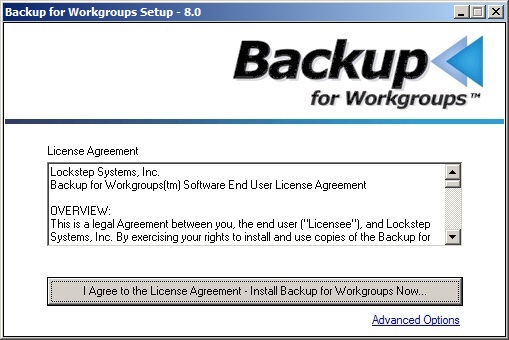
3. Press the button to agree to the license agreement. The setup program will now install Backup for Workgroups. When the installation process is complete, the Welcome screen appears.
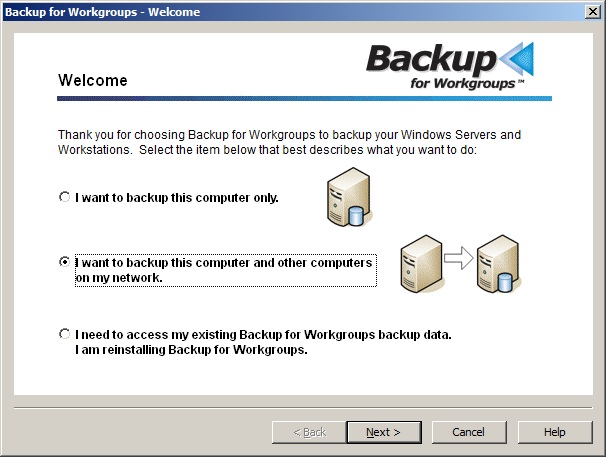
4. At the Welcome screen choose the middle button to indicate that you want to backup this computer and other computers on your network. Press Next.
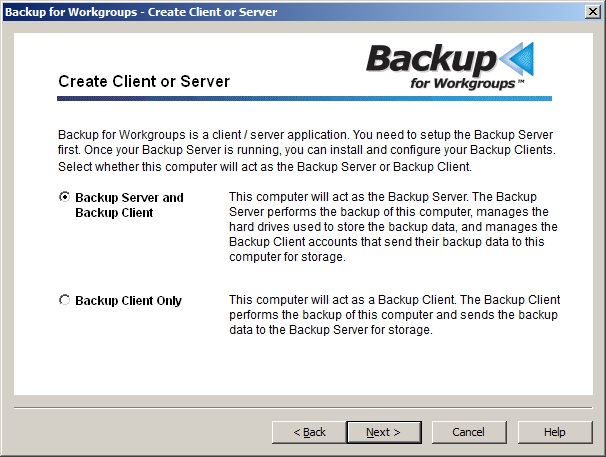
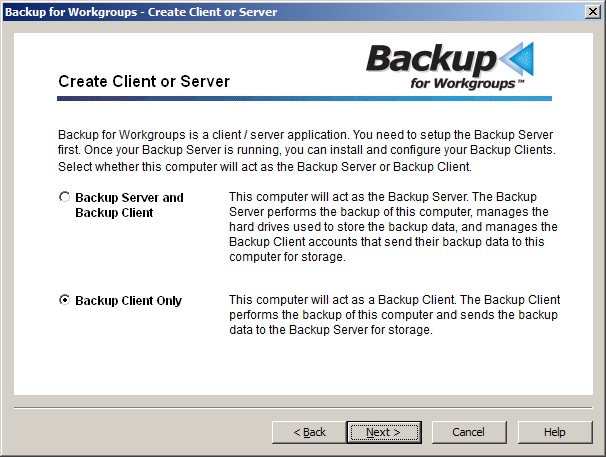
5. On the Create Client or Server screen - You need to select the top item because this computer is going to operate as your Backup Server. Press Next. 6. The next screen the Setup Wizard presents is the Backup Storage Location dialog. What you need to do on the Backup Storage Location dialog depends upon the type and location of your backup storage media. In general, there are two (2) types of storage media: storage that shows up as a Windows Drive letter or storage that is accessed through a UNC path to a network share. For detailed instructions on what you need to do on the Backup Storage Location dialog, click on the description below that matches your backup storage type:
Storing your backup data to internal drives or USB drives
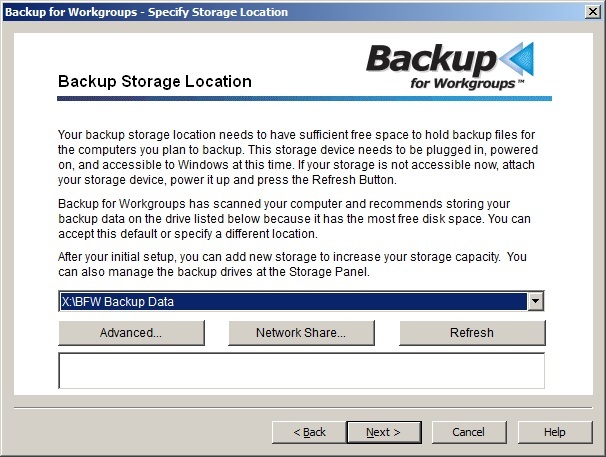
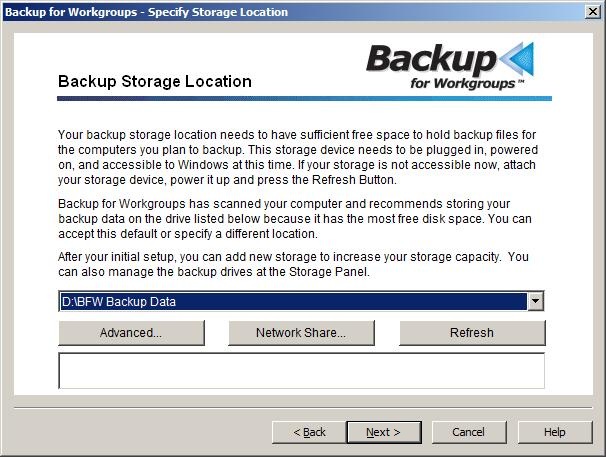
The Backup for Workgroups default automatically selects the largest drive on your computer that has most free space. The setup program should automatically select the internal or USB drive because in our example, it is the drive with the most free space. As seen above, Backup for Workgroups is going to store your backup data on the X: drive, under the BFW Backup Data directory. If the Setup program does not automatically select the correct storage location, then use the drop down box to select the internal drive or the USB Drive. If your USB drive does not show up in the drop-down list, make sure the drive is powered on, formatted in NTFS, and assigned a Windows drive letter and is accessible to Windows. Once you have double-checked these items and made any corrections needed, press the Refresh button to tell the Setup program to rescan your computer for the available drives. If you are using internal drives or USB drives as your primary backup storage media, you are all ready to continue in the Setup Wizard to select your computers that you want included in the backup process. Click here to jump to the next step in the setup - selecting the computers to backup. Storing your Backup Data to a NAS unit or Network Share Backup for Workgroups will default to selecting the largest drive on your computer that has most free space. In this case, this is not the selection that you want. Since you are intending to store your backup data to a network share or NAS, you need to tell Backup for Workgroups how to access the NAS unit/network share.
Press the Network Share button. Backup for Workgroups warns you of common problems encountered with NAS units. Accept the limitations of network shares/NAS units and you will now see the Select NAS Devices screen.
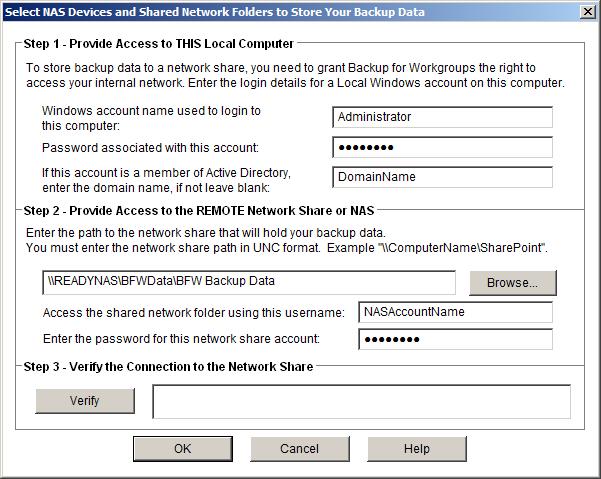
You use this dialog to establish access to/with the NAS unit/shared network folder. In order for Backup for Workgroups to store your backup data to the NAS unit, you will need to provide two basic groups of information. The first is a local Windows account and the second is an account at the NAS unit. In the top portion of this screen, in the section marked Step 1, enter the name and password of a Windows account that exists on this Windows Server or is within the domain this server is a member of. If this is a standalone server, then leave the Domain Name portion blank. If this Windows Server is a member of a domain, then enter the domain name in the Domain Name section. Backup for Workgroups runs as a service under the Windows Local SYSTEM account. This account is built-in to Windows for the purpose of allowing Services to access the files on the local Windows Server. But, the Local SYSTEM account is restricted and CANNOT directly access network shares. As a result, you need to provide a Windows account that is local to this computer or a Windows account that is a member of the domain that this Server is a member of. The account you provide is used by Backup for Workgroups to grant it the right to access shares outside of the server. You can think of the top half of this dialog as the process of being "granted the right to look outside of the Windows Server." The two most common Windows accounts to use are the Administrator account and the account that you are logged into at the Windows Server (if different than the administrator). In the section labeled Step 2, you specify how to access the network share at the NAS unit. First, enter the path to the network share in UNC format. UNC format starts with "\\" then the name of the NAS unit followed by a "\" and the share name. You can also enter a folder to use under the share name. We recommend using a folder under the share name so that if anyone looks at the network share, they will read the folder name and the name indicates the type of data stored there. In our example out NAS unit is named "ReadyNAS" it has a share named "BFWData" and we intend to store the backup data in a folder named "BFW Backup Data". This is entered as "\\ReadyNAS\BFWData\BFW Backup Data". Again the goal of using the folder named "BFW Backup Data" is that if someone would look at the share "\\ReadyNAS\BFWData" they would see the folder that tells them the contents are BFW backup data. Now you are ready to enter the name of an account at the NAS unit that has FULL ACCESS to this network share. If the NAS is configured to use a share that is accessible by everyone, the account name may not matter. If you had created an account name then enter that name and its password. NOTE: Some NAS units can join domains, so you may need to enter the account name in the form "DomainName\AccountName". Some NAS units that are standalone and not members of a domain require you to enter the NAS host name as a domain name. For example "ReadyNAS\UserName". You may have to experiment since there is no consistent naming convention between NAS manufactures. Press the Verify button. When you press the Verify button, Backup for Workgroups will use the settings that you have provided to access the network share. This proves your settings will allow Backup for Workgroups full control over the files at the network share. If you receive any errors, correct the items on this dialog until you get a successful verification. When you have verified your connection, press OK.
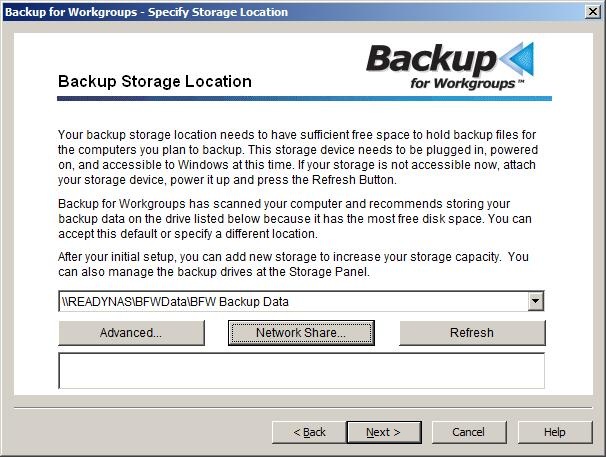
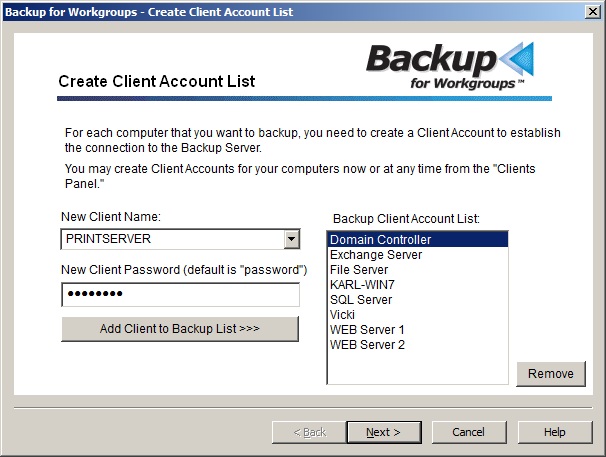
Backup for Workgroups displays the UNC path to the network share as the Backup Storage Location. Press Next. Now you are ready to select the computers that you want to include in the backup process. 7. Select the computers to backup Now you are ready to select the computers that you plan to backup. The computer running the Backup Server is automatically added to the list. Use the Add Client to Backup List button to add more computers (which we call Clients) to the list. When you are using the trial software, you can backup up to ten (10) computers during the evaluation period.
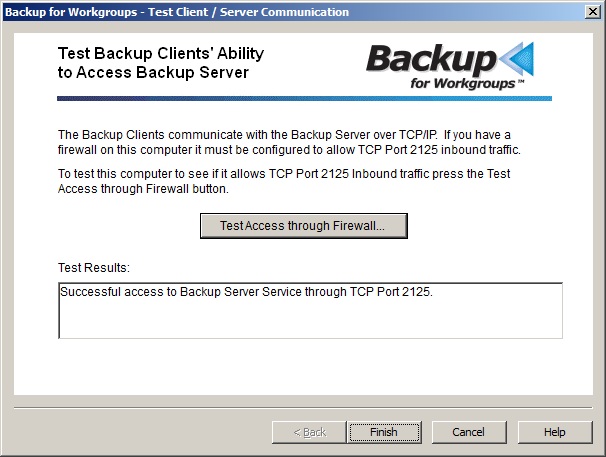
The setup program scans your network and creates a list of computers in the same domain as the backup server or in the same workgroup. You can select the computers by using the drop down list under the Net Client Name field. If you have other computers on your network that do not show up in the list, you can type them into the field labeled "New Client Computer", assign the account a password and press the "Add Client to Backup List" button. 8. Check the communication between the Backup Clients and the Backup Server. The Backup Clients communicate with the Backup Server over your network using TCP/IP port 2125. If there is a firewall on the computer running the Backup Server you need to instruct the firewall to open port 2125 for TCP inbound. Press the Test Access through Firewall button to make sure your Backup Clients can communicate with the Backup Server. If your test is successful, your firewall should be fine and you can continue to the next step. If the test indicates a problem, you will need to open your firewall for port 2125. This port is registered and has been assigned to Lockstep Systems by the Internet authority IANA. The Backup Clients connect to the Backup Server, so from a TCP/IP perspective, the Backup Client makes an outbound connection. The Backup Server receives the connection as an inbound event on port 2125. So, the firewall on the Backup Server must be configured to allow inbound TCP port 2125. At the computer running your Backup Server, open your firewall manager. This may be accessible under Control Panels or as part of an antivirus program. You need to create a rule to allow TCP port 2125 for inbound. Once you have configured your firewall to allow port 2125 for inbound TCP, then repeat the test on this panel. Once you have the firewall configured to allow port 2125 in bound TCP, then the backup clients will be able to connect to the Backup Server software that you have just installed on this computer.
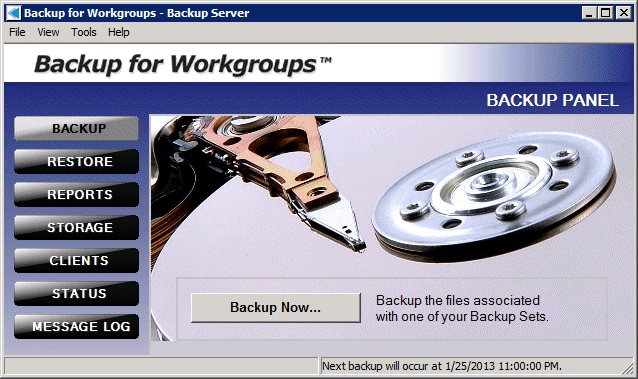
9. Press Finish to complete the setup. Now the Backup for Workgroups main program screen appears, as seen below.
Backup for Workgroups has a built-in backup set that is defined to backup all local drives on the Windows Servers at 11:00 pm and all local drives on your Windows workstations at noon. Backup for Workgroups also has a built-in open file add-on that allows the backup process to backup locked files on the server, this includes Exchange, SQL Server, and Domain Controller Active Directory databases. You can press the Backup Now... button to start your baseline backup now, or you can let the default, scheduled backup execute at its scheduled time. Please note that your computer must be powered on at 11pm for servers and noon for workstations, in order to perform the backup. If this time is inconvenient or you prefer another time, you can go to Tools>Manage Backup Sets to change the time on the All Local Drives backup set. Step 4 - Install the Backup ClientsThe Backup for Workgroups Backup Client is software that you install on each computer that you want to backup. This software runs on the computer, reads the files selected to be backed up, compresses and encrypts the backup data. Then, the Backup Client transmits the backup files to the Backup Server for storage. You will need to repeat these steps on each computer that you want to backup. NOTE that each computer to backup needs to have a separate account at the Backup Server. This avoids what we call "co-mingling" of data in which two (2) computers backup data into the same account making it difficult to restore data to the proper computer. Go to each computer you want to backup and run the Backup for Workgroups Setup program (BFWSETUP.EXE). This is the same setup program you downloaded above. The bfwsetup program is used to setup both Backup Servers and Backup Clients. 1. On the computer that you would like to include in the backup process, run the bfwsetup program. If you need to redownload the setup program you can do so with this link.
2. Press the button to agree to the license agreement. The setup program will now install Backup for Workgroups. When the installation process is complete, the welcome screen appears.
3. At the Welcome screen choose the middle item to indicate that you want to backup this computer and other computers on your network. Press Next.
4. At the Create Client or Server, choose Backup Client Only. You want to install the Backup Client software on this computer and send the backup data to the Backup Server for storage. Press Next.
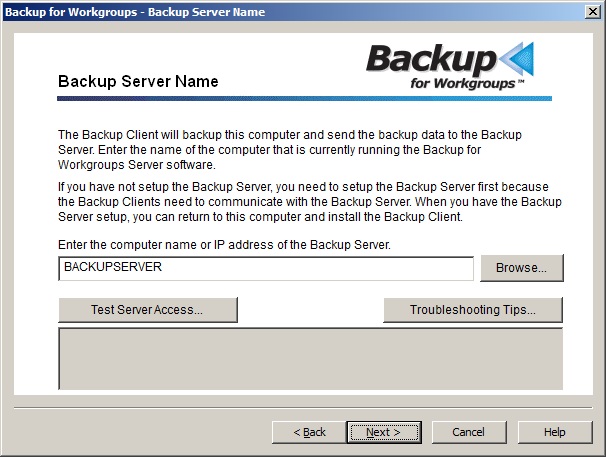
5. At the Backup Server Name panel, enter the name of the computer on which you installed the Backup Server software. You can enter the name of the computer running the Backup Server software or its IP address. Then press Test Server Access to make sure that the Backup Client can connect to the Backup Server. When you get a successful access to the Backup Server press Next. If the Backup Client cannot connect, then check the name of the backup server or firewall settings. Most firewalls at the client computers will allow all TCP communication outbound without needing to change the settings. If the firewall on this computer blocks outbound TCP, then configure the firewall to allow any port to communicate outbound TCP to port 2125.
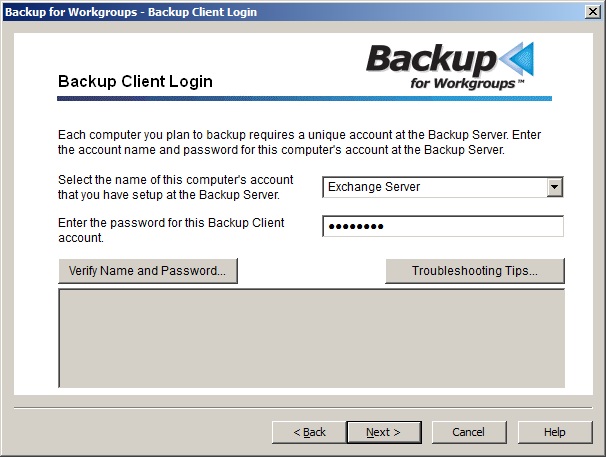
6. At the Backup Client Login panel, the drop down list will display the account names that you created at the Backup Server. Select the account name that you want to use to backup this computer. Enter the password that you had created for this account. If you do not know the name of the account or password, then go to the Backup Server and look at the Clients panel. Press the Verify Name and Password button. If the verify states that the account name or password is incorrect, change the password until you get a clean results from the verify. Then press Next to continue. 7. The setup wizard will display a panel indicating that your account is being synchronized with the Backup Server. When this process completes, the Backup for Workgroups main window appears.
Now you are ready to press the "Backup Now" button and start a complete backup of this computer. The Backup Client will backup the files on this computer and send the files to the Backup Server. The Backup Server then stores the files for all Backup Clients to the Backup Storage. HELPFUL TOPICS....
|